Call for Abstract
Scientific Program
International Conference on Gynecology and Obstetrics, will be organized around the theme “Exploring Versatile Approaches for Developments, Innovation & Strategies on Women’s Health”
Gynecology Obstetrics 2019 is comprised of 21 tracks and 114 sessions designed to offer comprehensive sessions that address current issues in Gynecology Obstetrics 2019.
Submit your abstract to any of the mentioned tracks. All related abstracts are accepted.
Register now for the conference by choosing an appropriate package suitable to you.
Intrapartum Care & Abnormal Labour Giving birth to a young one is a life changing event. The care that a woman receives during labour has the potential to affect her both physically and emotionally, as well us the health of her baby. Good communication, support and kindness from all the people, and having her wishes respected can help her feel in control of what is happening and contribute to making birth a positive experience for the woman and her birth companion.
PCOS is one of the most common hormone disorders in teenaged and adult women. It has been seen that one out of every five women almost suffers from this. More and more females suffer from erratic periods, acne, unwanted facial hair and. The chief cause of infertility is PCOS. The biggest health concerns are diabetes, heart disease, and stroke because PCOS is linked to having high blood pressure, pre-diabetes, and high cholesterol. The exact cause of PCOS has not been completely known but it appears that it must be having a number of factors on which it depends upon, such as increased level of hormones commonly known as androgens, and an irregular menstrual cycle.

- Track 2-1Insulin resistance
- Track 2-2Increase in facial or body hair (hirsutism)
- Track 2-3Hair loss
- Track 2-4Overweight
- Track 2-5Oily skin
- Track 2-6Acne
- Track 2-7Reduced fertility
- Track 2-8Prevention in IVF
- Track 2-9Prevention in IVF
Preconception health is said to be the health of men and women during their reproductive years. It focuses on taking steps of how to protect the health of a baby they might have sometime in the future, and staying healthy all throughout life.
When we talk about reproductive health it covers the right to healthy and respectful relationships, health services that are safe, and appropriate. It also includes of having access to correct information, effective and affordable methods of contraception. The access to sexual and reproductive health services, quality information about maintaining a healthy lifestyle, physical and mental health services can help all women achieve optimal health and wellbeing.

This type of cancer often occurs at the women’s cervix. It can be often found early and even prevented completely at times by having regular Pap tests. In case it is detected early it is one of the most treatable cancers. Regular pelvic assessments and Pap tests can detect precancerous changes in the cervix. HPV infection might cause cervical dysplasia, or any kind abnormal growth of cervical cells.The treatment for early-stage cervical cancer when it is confined to the cervix has a good success rate. The further the cancer has spread out of the area it originated from, the success rate lowers.There are common treatment methods used for this type of a cancer.
- Track 4-1Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection
- Track 4-2Chlamydia infection
- Track 4-3Use of oral contraceptives
- Track 4-4Intrauterine device (IUD)
- Track 4-5Colposcopy
- Track 4-6Cystoscopy
- Track 4-7Radiation Therapy
- Track 4-8Chemotherapy
- Track 4-9Immunotherapy
- Track 4-10Targeted Therapy
- Track 5-1Semen analysis
- Track 5-2Ovulation disorders
- Track 5-3Tubal occlusion
- Track 5-4In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
- Track 5-5Abdominal myomectomy
- Track 5-6Laparoscopy
- Track 5-7Hysteroscopy
- Track 5-8Hysterosalpingography (HSG)
\ Pediatric Gynecology emphasizes on gynecologic disorders amongst younger women. This is a turbulent time for women. The period of adolescence is the most ideal time to educate them about the preventive measures they should take, contraception, personal hygiene, and prevention of pregnancy. In the pediatric patient, gynecologic issues are often present as vulvar and vaginal problems, while in the adolescent patient, complaints of abdominopelvic pain and abnormal menstrual bleeding commonly result in a gynecologic evaluation.
\- Track 6-1Congenital abnormalities
- Track 6-2Contraceptive management for adolescent girls
- Track 6-3Lupus
- Track 6-4Heavy, irregular & painful menses
- Track 6-5Menstrual disorders in adolescent athletes
- Track 6-6Menstrual suppression
- Track 6-7Adnexal masses
- Track 6-8Precocious & delayed puberty
- Track 6-9Teenage acne
- Track 6-10Vaginal discharge
- Track 6-11Vulvovaginal concerns
It is the most natural thing that every woman experiences after a certain age in her life. It can occur between the ages of 42 and 56 but usually occurs when a women in almost 51. During this period the ovaries stop producing eggs and level of oestrogen declines. It is the natural cessation of ovarian function and menstruation. The symptoms of premature menopause are often the same as those experienced by women undergoing natural menopause.

- Track 7-1Hot flashes
- Track 7-2Mood swings.
- Track 7-3Night sweats
- Track 7-4Sleep problems
- Track 7-5Weight gain and Slow metabolism
- Track 7-6Thinning of hair
- Track 7-7Dry skin
- Track 7-8Irregular or missed periods
Gynaecologic Infectious Diseases
These are the infections which occur in the female reproductive tract and female genitalia, infections during pregnancy, pelvic infections, post-operative infections, and sexually transmitted infections. Infections which occur during pregnancy tend to pose a threat to the foetus. A simple urinary tract infection, which is most common during pregnancy, should be treated instantly. An infection that is left untreated may lead to preterm labour and may also rupture the membranes adjoining the foetus.
- Track 8-1Toxoplasmosis
- Track 8-2Hepatitis
- Track 8-3Rubella
- Track 8-4Parvovirus
- Track 8-5Gonorrhea
- Track 8-6Syphilis
- Track 8-7Herpes
- Track 8-8HSV
- Track 8-9HIV
- Track 8-10Chlamydia
This disease is found to be the second common gynaecologic cancer with several cases each day. It is a disease where some of the cells in one or both ovaries grow abnormally and eventually develop into cancer. The ovaries are two small almond shaped organs that are part of the female reproductive system. Each ovary measures about 2-4cm across and they sit on either side of the uterus. There are four main types of ovarian cancer, and these are named after the type of cells in the ovary where the cancer begins growing. Advanced ovarian cancer is often treated with the help of surgeries. Other cancers like vulvar cancer and vaginal cancer are comparatively rare and can be treated faster if detected and diagnosed properly at an early stage.
- Track 9-1Residual Diseases
- Track 9-2Cytoreductive Surgery
- Track 9-3Bevacizumab (Avastin) drugs
Prenatal care is also known as antenatal care. It is a vital part of staying healthy during pregnancy. It includes regular check-ups during pregnancy. It helps in decrease risks during pregnancy and increases the chance of a healthy delivery. Timely prenatal visits help in monitoring ones pregnancy and identify the complications before they become serious. Prenatal care ideally starts at least three months before you begin trying to conceive. Postnatal or postpartum care usually starts after the baby is born and lasts about 6–8 weeks. During this period, the mother is advised adequate rest, proper nutrition and other self-care measures as instructed by the family physician.

Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART) represents an increasingly important means of infertility treatment. The twenty-first century has been witness to further remarkable developments in the field of ART. The developments in patient management and stimulation remain to be important determinants in the outcome of ART. It covers a wide spectrum of treatments. Treatment is suggested depending on the cause of infertility.
- Track 11-1In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
- Track 11-2Artificial Insemination (AI)
- Track 11-3Surrogacy
- Track 11-4Intractoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI)
- Track 11-5Zygote Intrafallopian Transfer (ZIFT)
- Track 11-6Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD)
- Track 11-7Ovulation Induction
- Track 11-8Gamete Intrafallopian Transfer
Endometriosis is an enigmatic disease which is commonly associated with significant morbidity and reduction in quality life of reproductive age females. It often results in morbidity, pelvic pain, multiple surgeries and infertility. Timely diagnosis and effective management of the disease represent a challenge for both specialists and patients. The degree or stage at which endometriosis is present has no correlation with pain or symptomatic impairment. Symptoms are variable but may include pelvic pain, heavy bleeding and Dysmenorrhea.
- Track 12-1Adhesions
- Track 12-2Dyspareunia
- Track 12-3Progesterone resistance
- Track 12-4Risks of Adverse Pregnancy Outcome
- Track 12-5Preterm Birth
- Track 12-6Hormonal Contraceptives
- Track 12-7Danazol drugs
- Track 12-8Imaging Studies
- Track 12-9Surgical Intervention
- Track 12-10Laparoscopy
This branch deals with investigations and treatment for women with urinary incontinence, vaginal prolapse, bladder pain,recurrent urinary tract infections and pelvic floor injury after childbirth including faecal incontinence. Urogynaecological symptoms are not life-threatening but they can have an intense impact on the women’s quality of life. Clinical assessment aims to determine the extent of the impairment on quality of life.
- Track 13-1Enterocele
- Track 13-2Female genital prolapse
- Track 13-3Fecal incontinence
- Track 13-4Urinary incontinence
- Track 13-5Interstitial cystitis
- Track 13-6Müllerian agenesis
- Track 13-7Overactive bladder
- Track 13-8Painful intercourse
- Track 13-9Pelvic organ prolapse
- Track 13-10Rectocele
- Track 13-11Rectovaginal fistula
- Track 13-12Lichen sclerosus
- Track 13-13Interstitial cystitis
Gynecology and Obstetrics deals with all of life’s major passages from birth, reproduction, aging, to death. It has seen major medical advancements and has created an unexpected ethical dilemma for our discipline. The moral dilemmas that faced in this field range from public advocacy for the very basic needs of health and human rights for women to the most complex issues surrounding the growing knowledge and use of the human genome.
- Track 14-1Non Invasive Prenatal Test (NIPT)
When a woman is carrying more than one baby, it is known as multiple pregnancies. If more than one egg is released during the menstrual cycle and each one is fertilized by a sperm, more than one embryo may implant and grow in the uterus. Increment has been seen in multiple pregnancies. This is because more women older than 35 years are having babies. Women who belong to this age group are at high risk of having twins. Another reason for the increase is that more women are undergoing fertility treatments to become pregnant. These treatments increase the risk of multiple pregnancies. A multiple pregnancy can affect the health of both mother and the child. The most common complication of multiple pregnancies is preterm birth. Diagnostic tests for preterm births include Chorionic villus sampling and amniocentesis. However, these tests may be difficult to perform as each fetus has to be tested.
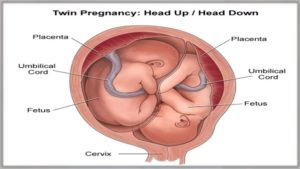
- Track 15-1Preterm Birth
- Track 15-2Low Birth Weight
- Track 15-3Cerebral palsy
- Track 15-4Incomplete separation
- Track 15-5Mortality rate (stillbirth)
- Track 15-6Chorionic villus sampling
- Track 15-7Amniocentesis
Contraception or birth control is designed to prevent a woman from getting pregnant. The contraceptives prevent the sperms from getting to the eggs. There are various types of birth control barriers available such as condoms, diaphragms, hormonal contraceptives, barrier contraceptives, IUD’s, cervical caps, and contraceptive sponges. Hormonal contraceptives have several health benefits, including decreasing a woman’s risk of uterine and ovarian cancer. Although hormonal contraceptive methods are associated with risks, for most women the use of one of these agents is safer than pregnancy.

- Track 16-1Hormonal contraceptives
- Track 16-2Barrier contraceptives
- Track 16-3Intrauterine devices (IUDs)
- Track 16-4Natural family planning
- Track 16-5Depo-Provera
- Track 16-6Cervical Cap
- Track 16-7Diaphragm
- Track 16-8Spermicide
- Track 16-9Contraceptive Injections
Human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) is a polypeptide hormone produced by the human placenta. It is composed of an alpha and a beta sub-unit. It is detected by gestation tests such as HCG gestation strip tests. Human chorionic gonadotropin interacts with the LHCG receptor of the ovary and promotes the maintenance of the corpus luteum during the beginning of pregnancy. It is used to cause biological process and to treat sterility in women, and to extend reproductive cell count in men. Human sac secretion (HCG) is given as associate injection to a lower place the skin or into a muscle. If you utilize human sac secretion (HCG) reception, your doctor, nurse, or chemist will provide you with specific directions on however and wherever to inject this medication. It should not be self-injected.
- Track 17-1Adrenal gland disorder
Metrorrhagia is also known as dysfunctional uterine bleeding from which women suffer from. It is a common disease and women usually suffer from this during the onset of mensuration. It is also seen in women nearing menopause. There are many causes of metrorrhagia, including hormone imbalance, abnormal growths, pregnancy complications, infections, birth control pills or problems with the hormone producing glands or areas in the brain. Certain conditions in the uterus or cervix can cause abnormal bleeding, including fibroids or polyps, scar tissue, inflammation, or cancer.
- Track 18-1Menometrorrhagia
- Track 18-2Amenorrhea
- Track 18-3Midcycle spotting
- Track 18-4No steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- Track 18-5Endometrial ablation
- Track 18-6Cervical dysplasia
\r\n It is a process of fertilisation where an egg is combined with sperms outside the body, in vitro ("in outside glass"). This process involves monitoring and stimulating a woman's ovulatory process, removing an ovum or ova (egg or eggs) from the woman's ovaries and letting sperm fertilise them in a liquid in a laboratory. After the fertilised egg commonly knows as zygote undergoes an embryo culture for 2–6 days, it is implanted in the same or another woman's uterus, with the intention of attaining a successful pregnency.
\r\n
<p style="\"text-align:" justify;\"="">Uterine prolapse transpire when the pelvic floor muscles and ligaments stretch and weaken.They can no longer provide enough support for uterus. In turn, the uterus protrudes out of the vagina.
It can occur in women of any age. It usually affects postmenopausal women who've had one or more vaginal deliveries.
Mild uterine prolapse usually doesn't require treatment, but uterine prolapse is making you uncomfortable causing any disruptions in your regular life, you may benefit from the treatment.
